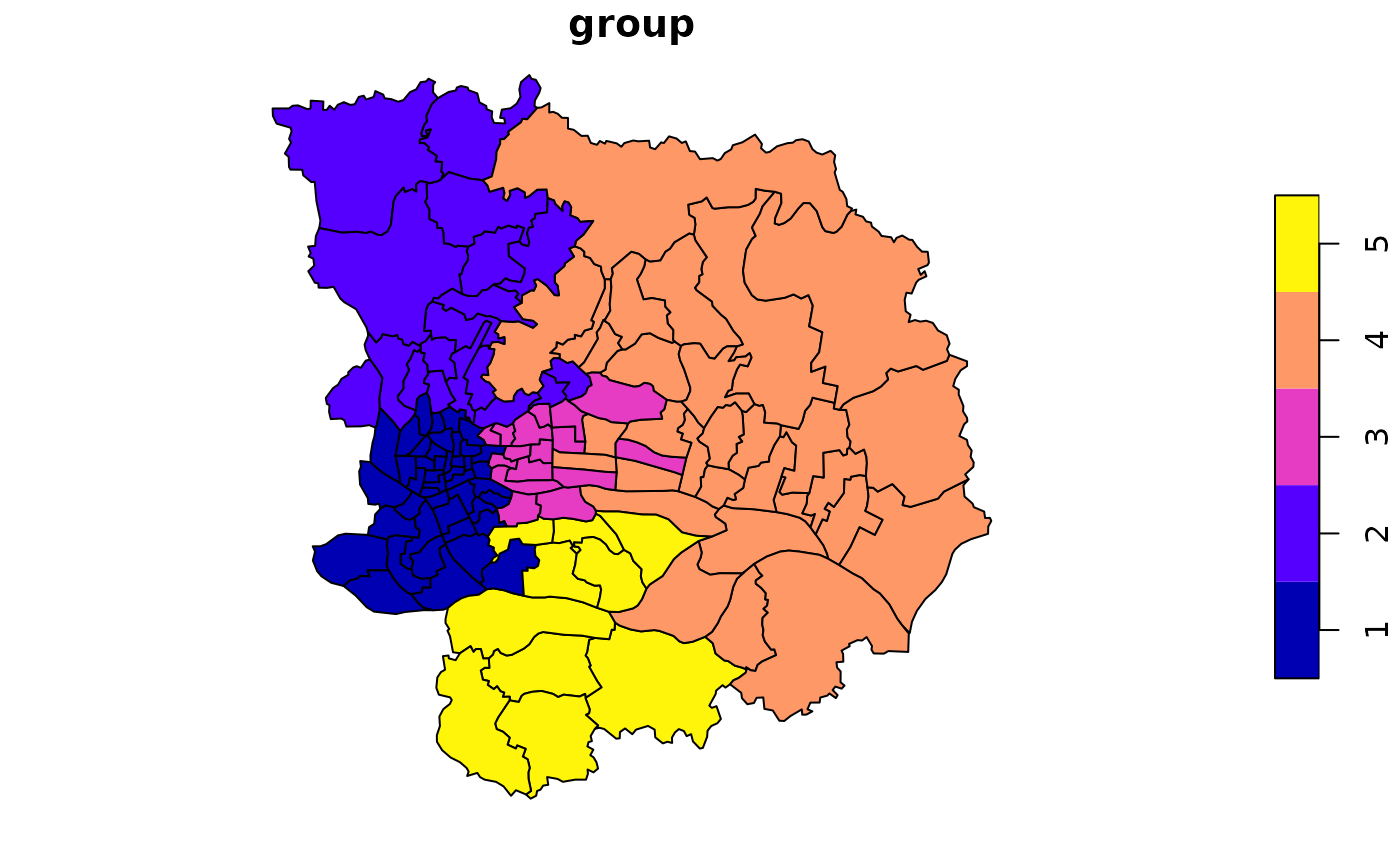
hierarchical clustering with spatial soft constraints
Usage
hclustgeo_disc(
data,
n,
alpha = 0.5,
D1 = NULL,
hclustm = "ward.D2",
scale = TRUE,
wt = NULL,
...
)Arguments
- data
An
sfobject,tibble,data.frame,matrixorvectorof observations data.- n
The number of hierarchical clustering classes, which can be a numeric value or vector.
- alpha
(optional) A positive value between
0and1. This mixing parameter gives the relative importance of "feature" space and "constraint" space. Default is0.5.- D1
(optional) A
matrixwith other dissimilarities between the same observations data. ifdatais ansfobject and alpha is not0, theD1will be generated bysdsfun::sf_distance_matrix(), others will use amatrixwith all elements equal to0.- hclustm
(optional) The agglomeration method to be used, default is
ward.D2. For more details, please seestats::hclust().- scale
(optional) Whether to scaled the dissimilarities matrix, default is
TRUE.- wt
(optional) Vector with the weights of the observations. By default,
wtisNULL.- ...
(optional) Other arguments passed to
stats::dist().
Value
The grouped membership: a vector if n is a scalar, a matrix (columns correspond to elements
of n) if not.
Examples
gzma = sf::read_sf(system.file('extdata/gzma.gpkg',package = 'sdsfun'))
gzma$group = hclustgeo_disc(gzma,5,alpha = 0.75)
plot(gzma["group"])