Synergistic-Unique-Redundant Decomposition of Causality (SURD)
Last
update: 2025-10-30
Last run: 2025-10-30
Source: Last run: 2025-10-30
vignettes/surd.Rmd
surd.RmdIntroduction
Understanding how causal influences combine and interact is essential for both temporal and spatial systems. The Synergistic–Unique–Redundant Decomposition (SURD) framework provides a principled way to break down total information flow between variables into:
- Unique contributions — information uniquely provided by one driver;
- Redundant contributions — information shared by multiple drivers;
- Synergistic contributions — information only revealed when drivers are considered together.
This vignette demonstrates how to perform SURD analysis using the
infocausality package. We will explore both temporal and
spatial cases, showing how infocausality unifies
time-series and spatial
cross-sectional causal analysis via consistent interfaces to
data.frame, sf, and SpatRaster
objects.
Utility Functions
To simplify post-processing and visualization, two helper functions are provided below.
utils_process_surd_result() converts a
surd_list object (as returned by an SURD computation
routine) into a tidy tibble for plotting and further
analysis.
utils_process_surd_result = \(surd_list,threshold = 0){
I_unique = surd_list$unique
I_synergistic = surd_list$synergistic
I_redundant = surd_list$redundant
info_leak = surd_list$info_leak
df = tibble::tibble(
label = c(
paste0("U[", names(I_unique), "]"),
paste0("S[", names(I_synergistic), "]"),
paste0("R[", names(I_redundant), "]")
),
value = c(as.numeric(I_unique),
as.numeric(I_synergistic),
as.numeric(I_redundant)),
type = c(rep("unique", length(I_unique)),
rep("synergistic", length(I_synergistic)),
rep("redundant", length(I_redundant)))
)
df$value = df$value / sum(df$value)
if(threshold > 0){
df = dplyr::filter(df, value > threshold)
}
return(dplyr::bind_rows(df,tibble::tribble(~label,~value,~type,
"Info Leak", info_leak, "info leak")))
}utils_plot_surd() produces a SURD decomposition plot — a
grouped bar chart of unique (U), synergistic
(S), and redundant (R) components, along with
a side panel showing the information leak.
utils_plot_surd = \(surd_list,threshold = 0,style = "shallow"){
I_unique = surd_list$unique
I_synergistic = surd_list$synergistic
I_redundant = surd_list$redundant
df = tibble::tibble(
label = c(
paste0("U[", names(I_unique), "]"),
paste0("S[", names(I_synergistic), "]"),
paste0("R[", names(I_redundant), "]")
),
value = c(as.numeric(I_unique),
as.numeric(I_synergistic),
as.numeric(I_redundant)),
type = c(rep("unique", length(I_unique)),
rep("synergistic", length(I_synergistic)),
rep("redundant", length(I_redundant)))
)
df$value = df$value / sum(df$value)
if(threshold > 0){
df = dplyr::filter(df, value > threshold)
}
df$label = factor(df$label, levels = df$label)
if (style == "shallow") {
colors = c(unique = "#ec9e9e", synergistic = "#fac58c", redundant = "#668392", infoleak = "#7f7f7f")
} else {
colors = c(unique = "#d62828", synergistic = "#f77f00", redundant = "#003049", infoleak = "gray")
}
p1 = ggplot2::ggplot(df, ggplot2::aes(x = label, y = value, fill = type)) +
ggplot2::geom_col(color = "black", linewidth = 0.15, show.legend = FALSE) +
ggplot2::scale_fill_manual(name = NULL, values = colors) +
ggplot2::scale_x_discrete(name = NULL, labels = function(x) parse(text = x)) +
ggplot2::scale_y_continuous(name = NULL, limits = c(0, 1), expand = c(0, 0),
breaks = c(0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1),
labels = c("0", "0.25", "0.5", "0.75", "1") ) +
ggplot2::theme_bw() +
ggplot2::theme(
axis.ticks.x = ggplot2::element_blank(),
axis.text.x = ggplot2::element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1),
panel.grid = ggplot2::element_blank(),
panel.border = ggplot2::element_rect(color = "black", linewidth = 2)
)
df_leak = tibble::tibble(label = "Info Leak", value = surd_list$info_leak)
p2 = ggplot2::ggplot(df_leak, ggplot2::aes(x = label, y = value)) +
ggplot2::geom_col(fill = colors[4], color = "black", linewidth = 0.15) +
ggplot2::scale_x_discrete(name = NULL, expand = c(0, 0)) +
ggplot2::scale_y_continuous(name = NULL, limits = c(0, 1), expand = c(0, 0),
breaks = c(0,1), labels = c(0,1) ) +
ggplot2::theme_bw() +
ggplot2::theme(
axis.ticks.x = ggplot2::element_blank(),
panel.grid = ggplot2::element_blank(),
panel.border = ggplot2::element_rect(color = "black", linewidth = 2)
)
patchwork::wrap_plots(p1, p2, ncol = 2, widths = c(10,1))
}Example Cases
The following sections demonstrate SURD decomposition in different contexts, illustrating its flexibility across temporal and spatial causal analyses.
Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Health in Hong Kong
cvd = readr::read_csv(system.file("case/cvd.csv",package = "tEDM"))
head(cvd)
## # A tibble: 6 × 5
## cvd rsp no2 so2 o3
## <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 214 73.7 74.5 19.1 17.4
## 2 203 77.6 80.9 18.8 39.4
## 3 202 64.8 67.1 13.8 56.4
## 4 182 68.8 74.7 30.8 5.6
## 5 181 49.4 62.3 23.1 3.6
## 6 129 67.4 63.6 17.4 6.73
cvd_long = cvd |>
tibble::rowid_to_column("id") |>
tidyr::pivot_longer(cols = -id,
names_to = "variable", values_to = "value")
fig_cvds_ts = ggplot2::ggplot(cvd_long, ggplot2::aes(x = id, y = value, color = variable)) +
ggplot2::geom_line(linewidth = 0.5) +
ggplot2::labs(x = "Days (from 1995-3 to 1997-11)", y = "Concentrations or \nNO. of CVD admissions", color = "") +
ggplot2::theme_bw() +
ggplot2::theme(legend.direction = "horizontal",
legend.position = "inside",
legend.justification = c("center","top"),
legend.background = ggplot2::element_rect(fill = "transparent", color = NA))
fig_cvds_ts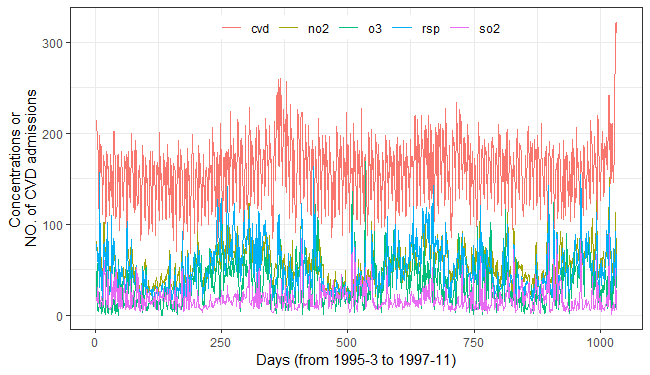
To investigate the causal influences of air pollutants on the
incidence of cardiovascular diseases, we performed SURD analysis using a
time lag step 3 and 10 discretization
bins.
res_cvds = infocausality::surd(cvd, "cvd",
c("rsp", "no2", "so2", "o3"),
lag = 15, bin = 10, cores = 6)
##
## SURD Decomposition Results:
## Unique (U):
## X1 : 0.0022
## X2 : 0.0162
## X3 : 0.0024
## X4 : 0.0000
## Synergistic (S):
## X1-X2 : 0.0181
## X1-X3 : 0.0198
## X1-X4 : 0.0339
## X2-X3 : 0.0293
## X2-X4 : 0.0332
## X3-X4 : 0.0477
## X1-X2-X3 : 0.0343
## X1-X2-X4 : 0.1084
## X1-X3-X4 : 0.1540
## X2-X3-X4 : 0.0426
## X1-X2-X3-X4 : 0.4093
## Redundant (R):
## X1-X2 : 0.0034
## X1-X3 : 0.0000
## X1-X4 : 0.0007
## X2-X3 : 0.0006
## X2-X4 : 0.0034
## X3-X4 : 0.0000
## X1-X2-X3 : 0.0050
## X1-X2-X4 : 0.0100
## X1-X3-X4 : 0.0008
## X2-X3-X4 : 0.0014
## X1-X2-X3-X4 : 0.0230
## Information Leak: 52.82%The SURD results are shown in the figure below:
utils_plot_surd(res_cvds)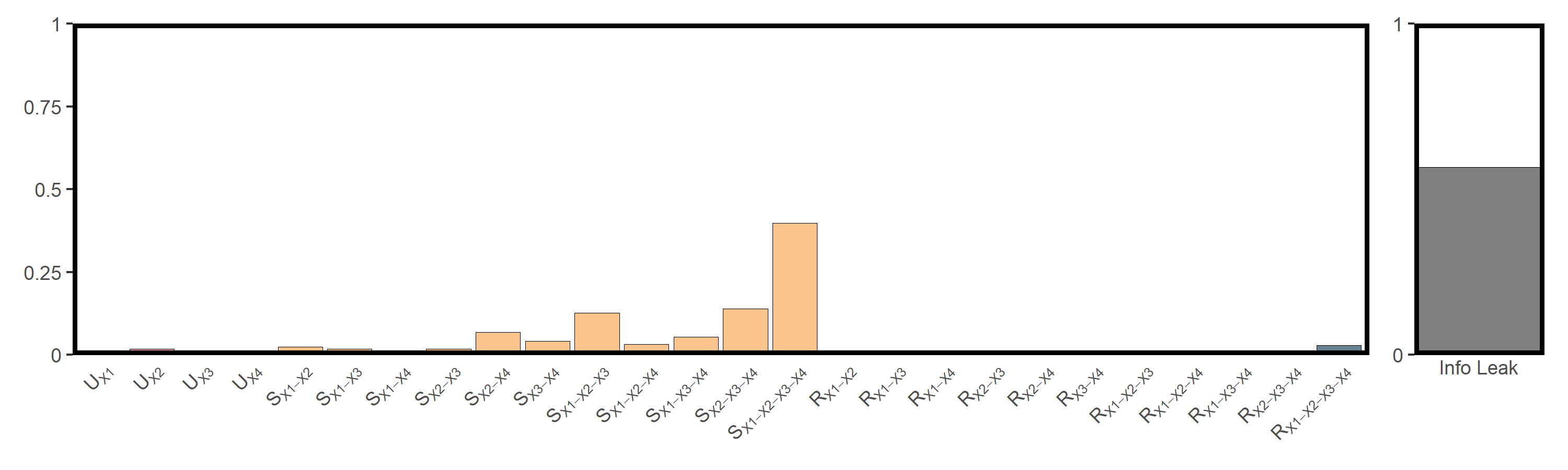
Population Density and Its Drivers in Mainland China
popd_nb = spdep::read.gal(system.file("case/popd_nb.gal",package = "spEDM"))
## Warning in spdep::read.gal(system.file("case/popd_nb.gal", package = "spEDM")):
## neighbour object has 4 sub-graphs
popd = readr::read_csv(system.file("case/popd.csv",package = "spEDM"))
popd_sf = sf::st_as_sf(popd, coords = c("lon","lat"), crs = 4326)
popd_sf
## Simple feature collection with 2806 features and 5 fields
## Geometry type: POINT
## Dimension: XY
## Bounding box: xmin: 74.9055 ymin: 18.2698 xmax: 134.269 ymax: 52.9346
## Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
## # A tibble: 2,806 × 6
## popd elev tem pre slope geometry
## * <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <POINT [°]>
## 1 780. 8 17.4 1528. 0.452 (116.912 30.4879)
## 2 395. 48 17.2 1487. 0.842 (116.755 30.5877)
## 3 261. 49 16.0 1456. 3.56 (116.541 30.7548)
## 4 258. 23 17.4 1555. 0.932 (116.241 30.104)
## 5 211. 101 16.3 1494. 3.34 (116.173 30.495)
## 6 386. 10 16.6 1382. 1.65 (116.935 30.9839)
## 7 350. 23 17.5 1569. 0.346 (116.677 30.2412)
## 8 470. 22 17.1 1493. 1.88 (117.066 30.6514)
## 9 1226. 11 17.4 1526. 0.208 (117.171 30.5558)
## 10 137. 598 13.9 1458. 5.92 (116.208 30.8983)
## # ℹ 2,796 more rows
res_popd = infocausality::surd(popd_sf,"popd",c("elev","tem","pre","slope"),
lag = 3, bin = 10, nb = popd_nb, cores = 6)
##
## SURD Decomposition Results:
## Unique (U):
## X1 : 0.0046
## X2 : 0.0000
## X3 : 0.0398
## X4 : 0.0036
## Synergistic (S):
## X1-X2 : 0.0369
## X1-X3 : 0.0471
## X1-X4 : 0.0885
## X2-X3 : 0.0468
## X2-X4 : 0.0765
## X3-X4 : 0.0877
## X1-X2-X3 : 0.0384
## X1-X2-X4 : 0.0597
## X1-X3-X4 : 0.0463
## X2-X3-X4 : 0.1577
## X1-X2-X3-X4 : 0.1095
## Redundant (R):
## X1-X2 : 0.0000
## X1-X3 : 0.0089
## X1-X4 : 0.0000
## X2-X3 : 0.0130
## X2-X4 : 0.0027
## X3-X4 : 0.0138
## X1-X2-X3 : 0.0056
## X1-X2-X4 : 0.0000
## X1-X3-X4 : 0.0120
## X2-X3-X4 : 0.0110
## X1-X2-X3-X4 : 0.0897
## Information Leak: 64.64%
utils_plot_surd(res_popd)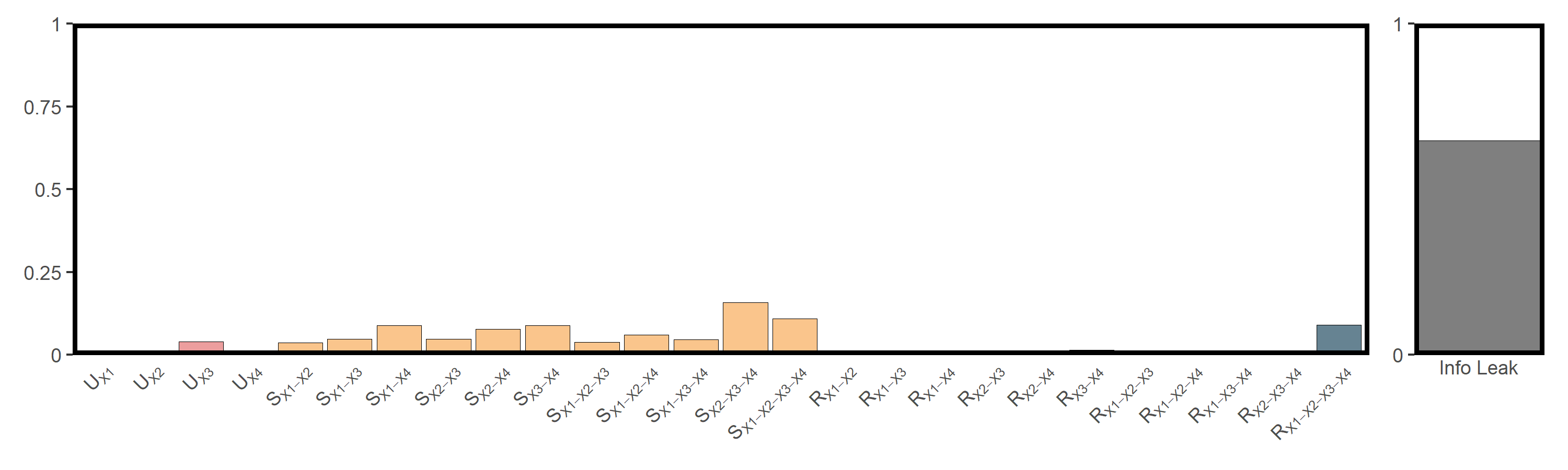
Influence of Climatic and Topographic Factors on Net Primary Productivity (NPP) in Mainland China
npp = terra::rast(system.file("case/npp.tif", package = "spEDM"))
npp
## class : SpatRaster
## size : 404, 483, 5 (nrow, ncol, nlyr)
## resolution : 10000, 10000 (x, y)
## extent : -2625763, 2204237, 1877078, 5917078 (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
## coord. ref. : CGCS2000_Albers
## source : npp.tif
## names : npp, pre, tem, elev, hfp
## min values : 164.00, 384.3409, -47.8194, -122.2004, 0.03390418
## max values : 16606.33, 23878.3555, 263.6938, 5350.4902, 44.90312195
res_npp = infocausality::surd(npp,"npp",c("pre","tem","elev","hfp"),
lag = 2, bin = 10, cores = 6)
##
## SURD Decomposition Results:
## Unique (U):
## X1 : 0.2060
## X2 : 0.0004
## X3 : 0.0001
## X4 : 0.0000
## Synergistic (S):
## X1-X2 : 0.0477
## X1-X3 : 0.0734
## X1-X4 : 0.0360
## X2-X3 : 0.0268
## X2-X4 : 0.0049
## X3-X4 : 0.0010
## X1-X2-X3 : 0.0363
## X1-X2-X4 : 0.0171
## X1-X3-X4 : 0.0380
## X2-X3-X4 : 0.0201
## X1-X2-X3-X4 : 0.0796
## Redundant (R):
## X1-X2 : 0.2658
## X1-X3 : 0.0020
## X1-X4 : 0.0000
## X2-X3 : 0.0000
## X2-X4 : 0.0000
## X3-X4 : 0.0000
## X1-X2-X3 : 0.0439
## X1-X2-X4 : 0.0000
## X1-X3-X4 : 0.0065
## X2-X3-X4 : 0.0000
## X1-X2-X3-X4 : 0.0941
## Information Leak: 40.78%
utils_plot_surd(res_npp)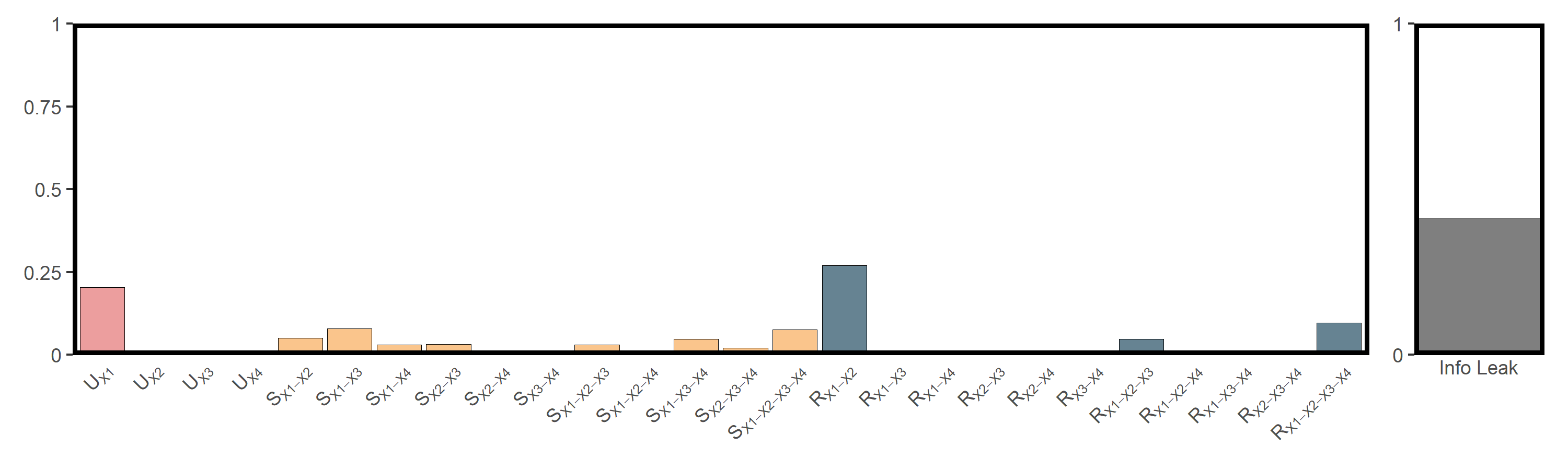
🧩 See also:
-
?infocausality::surd()for function details. -
spEDMpackage for spatial empirical dynamic modeling. -
tEDMpackage for temporal empirical dynamic modeling.