geographical convergent cross mapping
Usage
# S4 method for class 'sf'
gccm(
data,
cause,
effect,
libsizes = NULL,
E = 3,
k = E + 2,
tau = 1,
style = 1,
stack = FALSE,
lib = NULL,
pred = NULL,
dist.metric = "L2",
dist.average = TRUE,
theta = 1,
algorithm = "simplex",
threads = detectThreads(),
detrend = TRUE,
parallel.level = "low",
bidirectional = TRUE,
progressbar = TRUE,
nb = NULL
)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
gccm(
data,
cause,
effect,
libsizes = NULL,
E = 3,
k = E + 2,
tau = 1,
style = 1,
stack = FALSE,
lib = NULL,
pred = NULL,
dist.metric = "L2",
dist.average = TRUE,
theta = 1,
algorithm = "simplex",
threads = detectThreads(),
detrend = TRUE,
parallel.level = "low",
bidirectional = TRUE,
progressbar = TRUE,
grid.coord = TRUE,
embed.direction = 0,
win.ratio = 0
)Arguments
- data
observation data.
- cause
name of causal variable.
- effect
name of effect variable.
- libsizes
(optional) number of spatial units used (input needed:
vector- spatial vector,matrix- spatial raster).- E
(optional) embedding dimensions.
- k
(optional) number of nearest neighbors.
- tau
(optional) step of spatial lags.
- style
(optional) embedding style (
0includes current state,1excludes it).- stack
(optional) whether to stack embeddings.
- lib
(optional) libraries indices (input requirement same as
libsizes).- pred
(optional) predictions indices (input requirement same as
libsizes).- dist.metric
(optional) distance metric (
L1: Manhattan,L2: Euclidean).- dist.average
(optional) whether to average distance.
- theta
(optional) weighting parameter for distances, useful when
algorithmissmap.- algorithm
(optional) prediction algorithm.
- threads
(optional) number of threads to use.
- detrend
(optional) whether to remove the linear trend.
- parallel.level
(optional) level of parallelism,
loworhigh.- bidirectional
(optional) whether to examine bidirectional causality.
- progressbar
(optional) whether to show the progress bar.
- nb
(optional) neighbours list.
- grid.coord
(optional) whether to detrend using cell center coordinates (
TRUE) or row/column numbers (FALSE).- embed.direction
(optional) direction selector for embeddings (
0returns all directions,1-8correspond to NW, N, NE, W, E, SW, S, SE).- win.ratio
(optional) ratio of sliding window scale to speed up state-space predictions.
Value
A list
xmapcross mapping results
varnamenames of causal and effect variables
bidirectionalwhether to examine bidirectional causality
References
Gao, B., Yang, J., Chen, Z. et al. Causal inference from cross-sectional earth system data with geographical convergent cross mapping. Nat Commun 14, 5875 (2023).
Examples
columbus = sf::read_sf(system.file("case/columbus.gpkg",package="spEDM"))
# \donttest{
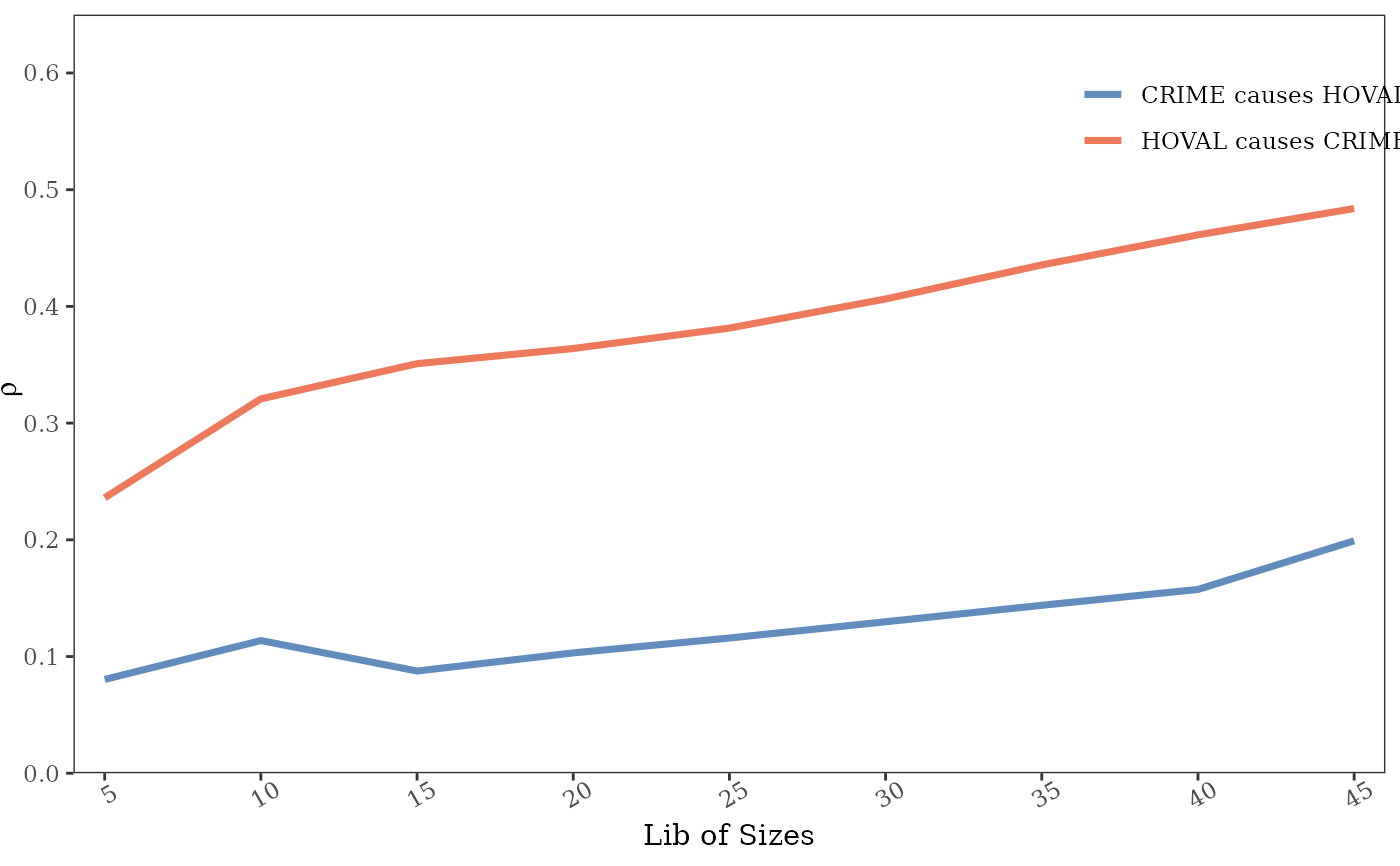
g = gccm(columbus,"hoval","crime",libsizes = seq(5,45,5),E = 6)
#>
Computing: [========================================] 100% (done)
#>
Computing: [========================================] 100% (done)
g
#> libsizes hoval->crime crime->hoval
#> 1 5 0.1253050 0.2568469
#> 2 10 0.1762769 0.3961522
#> 3 15 0.2197481 0.4672470
#> 4 20 0.2324435 0.5144297
#> 5 25 0.2354728 0.5713321
#> 6 30 0.2360934 0.6048914
#> 7 35 0.2412944 0.6253026
#> 8 40 0.2383788 0.6364897
#> 9 45 0.2339483 0.6484721
plot(g,ylimits = c(0,0.85))
 # }
# }