geographical pattern causality
Usage
# S4 method for class 'sf'
gpc(
data,
cause,
effect,
libsizes = NULL,
E = 3,
k = E + 2,
tau = 1,
style = 1,
lib = NULL,
pred = NULL,
boot = 99,
random = TRUE,
seed = 42L,
dist.metric = "L2",
zero.tolerance = max(k),
relative = TRUE,
weighted = TRUE,
threads = detectThreads(),
detrend = FALSE,
parallel.level = "low",
bidirectional = TRUE,
progressbar = TRUE,
nb = NULL
)
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
gpc(
data,
cause,
effect,
libsizes = NULL,
E = 3,
k = E + 2,
tau = 1,
style = 1,
lib = NULL,
pred = NULL,
boot = 99,
random = TRUE,
seed = 42L,
dist.metric = "L2",
zero.tolerance = max(k),
relative = TRUE,
weighted = TRUE,
threads = detectThreads(),
detrend = FALSE,
parallel.level = "low",
bidirectional = TRUE,
progressbar = TRUE,
grid.coord = TRUE
)Arguments
- data
observation data.
- cause
name of causal variable.
- effect
name of effect variable.
- libsizes
(optional) number of spatial units used (input needed:
vector- spatial vector,matrix- spatial raster).- E
(optional) embedding dimensions.
- k
(optional) number of nearest neighbors.
- tau
(optional) step of spatial lags.
- style
(optional) embedding style (
0includes current state,1excludes it).- lib
(optional) libraries indices (input requirement same as
libsizes).- pred
(optional) predictions indices (input requirement same as
libsizes).- boot
(optional) number of bootstraps to perform.
- random
(optional) whether to use random sampling.
- seed
(optional) random seed.
- dist.metric
(optional) distance metric (
L1: Manhattan,L2: Euclidean).- zero.tolerance
(optional) maximum number of zeros tolerated in signature space.
- relative
(optional) whether to calculate relative changes in embedding.
- weighted
(optional) whether to weight causal strength.
- threads
(optional) number of threads to use.
- detrend
(optional) whether to remove the linear trend.
- parallel.level
(optional) level of parallelism,
loworhigh.- bidirectional
(optional) whether to examine bidirectional causality.
- progressbar
(optional) whether to show the progress bar.
- nb
(optional) neighbours list.
- grid.coord
(optional) whether to detrend using cell center coordinates (
TRUE) or row/column numbers (FALSE).
Value
A list
xmapcross mapping results (only present if
libsizesis notNULL)causalityper-sample causality statistics (present if
libsizesisNULL)summaryoverall causal strength (present if
libsizesisNULL)patternpairwise pattern relationships (present if
libsizesisNULL)varnamenames of causal and effect variables
bidirectionalwhether to examine bidirectional causality
References
Zhang, Z., Wang, J., 2025. A model to identify causality for geographic patterns. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 1–21.
Examples
columbus = sf::read_sf(system.file("case/columbus.gpkg",package="spEDM"))
# \donttest{
gpc(columbus,"hoval","crime",E = 6,k = 9)
#> type strength direction
#> 1 positive NaN hoval -> crime
#> 2 negative 0.12226140 hoval -> crime
#> 3 dark 0.08292105 hoval -> crime
#> 4 positive NaN crime -> hoval
#> 5 negative 0.64799884 crime -> hoval
#> 6 dark 0.15444661 crime -> hoval
# convergence diagnostics
g = gpc(columbus,"hoval","crime",libsizes = seq(5,45,5),E = 6,k = 9)
#>
Computing: [========================================] 100% (done)
#>
Computing: [========================================] 100% (done)
plot(g)
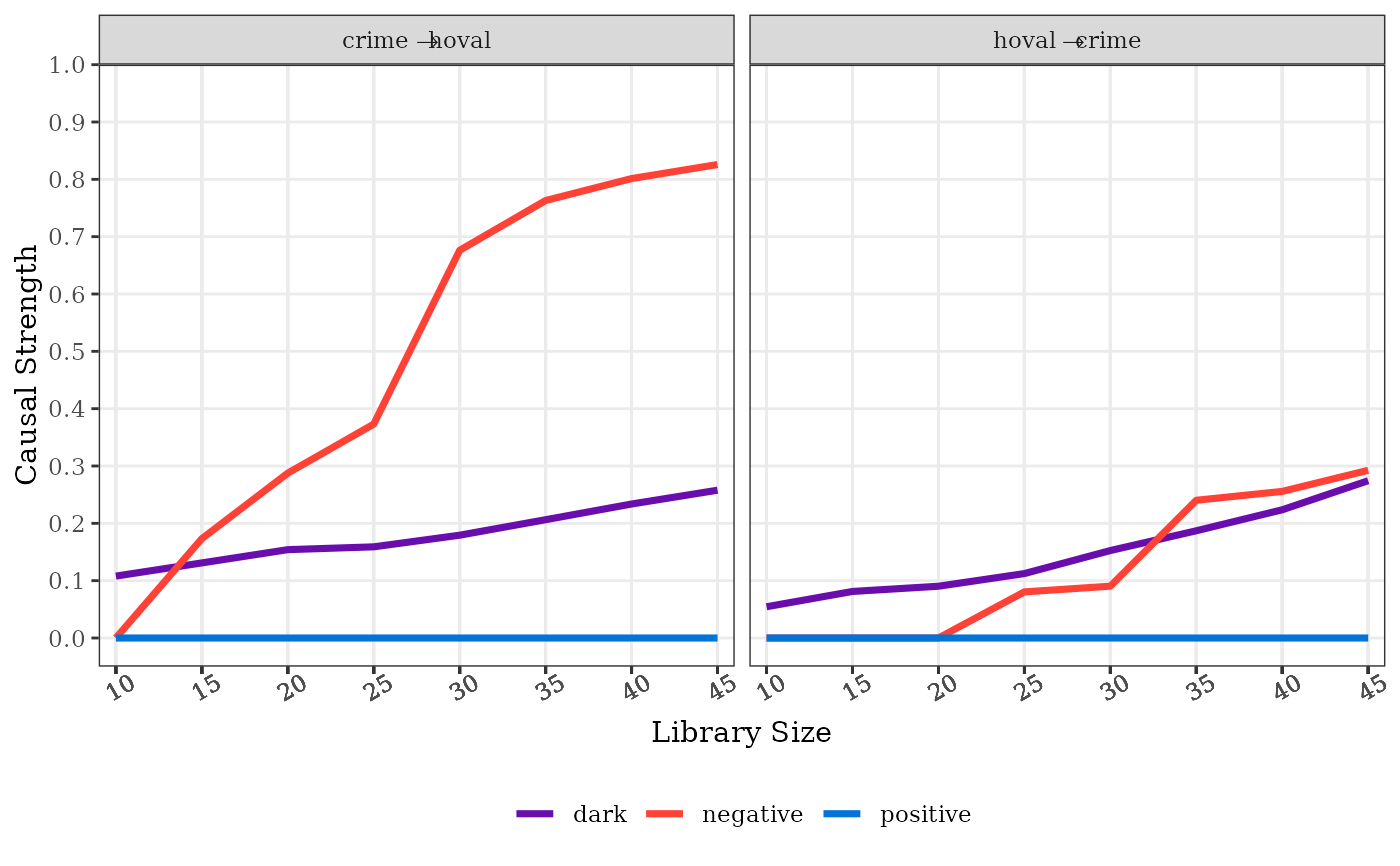 # }
# }